© 2014, S. A. Chetvertakov*
*. Ph.D., Independent researcher, Saint-Petersburg; email: sergeychet@yandex.ru
This report is an overview of the conclusions of a fifteen-year initiative of the author in the field of Maslow's theory including yet unpublished results. We present the modified, reconstructed and supplemented Maslow’s theory of hierarchy of needs, version 3, as a development of the first two versions of this theory: the first - 1943-1956 and second – 1970. Some of our applications of Maslow's theory in sociology during the period from 1973 to 2000 revealed a number of disadvantages in it. Most of these disadvantages were eliminated or solved in the author's monograph "Reconstruction of Maslow’s Theory" (Aleteya, 2011-576 pp.). An objective of this report is to systematize basic concepts of psychology that are important for Maslow’s theory, providing significant reasons for the scope and the hierarchy of needs. New additions are relevant to the needs for love, belongingness, creativity as an extension of self-actualization and need for self-esteem (as conscience). The work may be useful to psychologists, sociologists and all readers interested in new ideas in the field of psychology, social psychology and sociology.
Keywords: Maslow, love-belongingness, esteem, creativity, self-esteem as conscience, the reasons for the hierarchy, the appearance of consciousness.
Introduction
Evolution and role of adaptation
Adaptation of the living and emergence of the psyche
Psyche as an independent level of manifestation of the living
The central nervous system as a biological environment of the psyche
Two fields of the psyche on the base of neurophysiology
Biology and semantics in the mental activity
Mental functions and objects
The association: its image, representation and role in the prediction
The behavior - interpretation through sensations
The need as special secondary sensations
The objects of the psyche in Wiener adaptation model
Adaptation and languages. Difference between human language and animal communication
Human language and work of psyche with it
The motivation, goal and need
Rise of the Maslow’s theory. Its basic ideas
From the environment to the needs and behavior
Innate and acquired associative links
Influence of new associations on human beings
Feedback in the adaptation of system
Automatism and attitude. How to hide needs
The needs of Maslow-3. Reasons for the hierarchy
The need for eliminating fear of pain or the need for safety 1(I)
Physiological needs as water, food and heat balance
The need for safety 2 (II) or life comfort
The need for love and belongingness
Love and family
Love in family as culture
Sex or love?
The belongingness as the special need
The need for communication as affiliation
Technical communication is rather motivation or behavior, than need
Novelty seeking as a need for diversity
The need for respect or safety 3 (III)
Stratification among animals. The war and the peace. Rank’s resource as determinant of status.
A need for respect in the hierarchy
The difference in status between human and animals
The dynamics of rank's resources in human history. The practice of distortion
The metaneeds for creativity
The definition of creativity
Memory and expectation
How was creativity enforced in Evolution? The benefits and harms
Expansion of metaneeds
The metabasic needs
The pure metaneeds
The needs for knowledge and truth, aesthetics and self-actualization as a forms of creativity
The creativity and freedom
The need for the self-esteem or the conscience as the need for safety 4 (IV)
The place of self-esteem or conscience in hierarchy of needs
The societies without conscience and the societies of conscience people
Characteristics of conscience and perspectives of phenomenon
Source of conscience: consciousness or environment
The Maslow’s hierarchy of needs – 3 as a whole
Common definition of the need
Common definition of the environment
Axiomatic nature of the hierarchy of needs
Feasibility of axioms
Prediction and its quality on a base of axiomatics
Significance Maslow’s theory for psychology
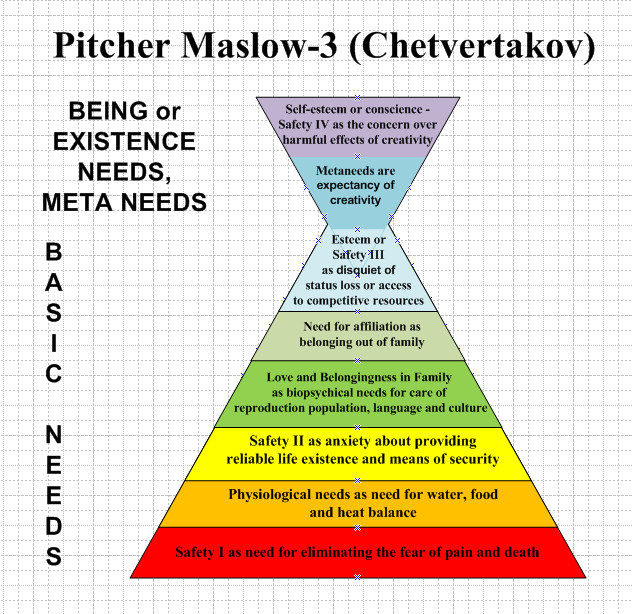
Fig. 1. Pitcher of Maslow-3 instead of pyramid of Maslow-1,2
The need is felt to be of particular subconscious state. When it is satisfied, we do not feel it. So the perceived state of actual need should be defined as a state of dissatisfaction. But in literature needs are usually described by feelings of satisfaction. We eliminate this defect. For example, the first need below - it's a feeling of fear or terror. The need is to remove this fear (and the reason of fear). In this sense, we define the needs by real emotion related to them.
New hierarchy of Maslow, version 3, includes next needs:
1. Safety need 1 – eliminating fear of pain or death.
2. Physical need – needs for water, food and heat balance.
3. Safety need 2 – anxiety about providing reliable life existence and means of security, i. e. previous two needs in future.
4. Need for Love and Belongingness in Family as biopsychic needs for population reproduction to provide own old ages and to prolong language and culture.
5. Affiliation need as belongingness out of family and feeling of loneliness - initial mean to get access to technical information for other needs.
6. Esteem or safety 3 – disquiet of status loss or loss of access to competitive resources.
7. Metaneeds as expectancy to creative social useful activity (pure metaneeds) or as creativeness in consumption, spending own forces and resources in pleasure (metabased needs). The person may have several metaneeds.
8. Conscience, the need for self-esteem or the need for safety 4 is the concern over past or future harmful effects of the own creativity or harmful activity of others (or Mankind) in fields of social and global significance. It motivates to eliminate errors of the past or prevent social or global problems in future. Conscience fulfills feedback for creativity as direct action in Wiener control system. This is also the cultural and acquired (by means of consciousness) correction tool for the maintenance and transmission of ethical norms in society.
And this system of the needs is a common historic model of generalised human psychology – psychic development model in anthropogenesis and social history. The theory needs is suitable for the interpretation of history, as shown in the examples demonstrating reconstruction of macrosocial phenomenons.
Exposed in 4 Dec 2014
.
.